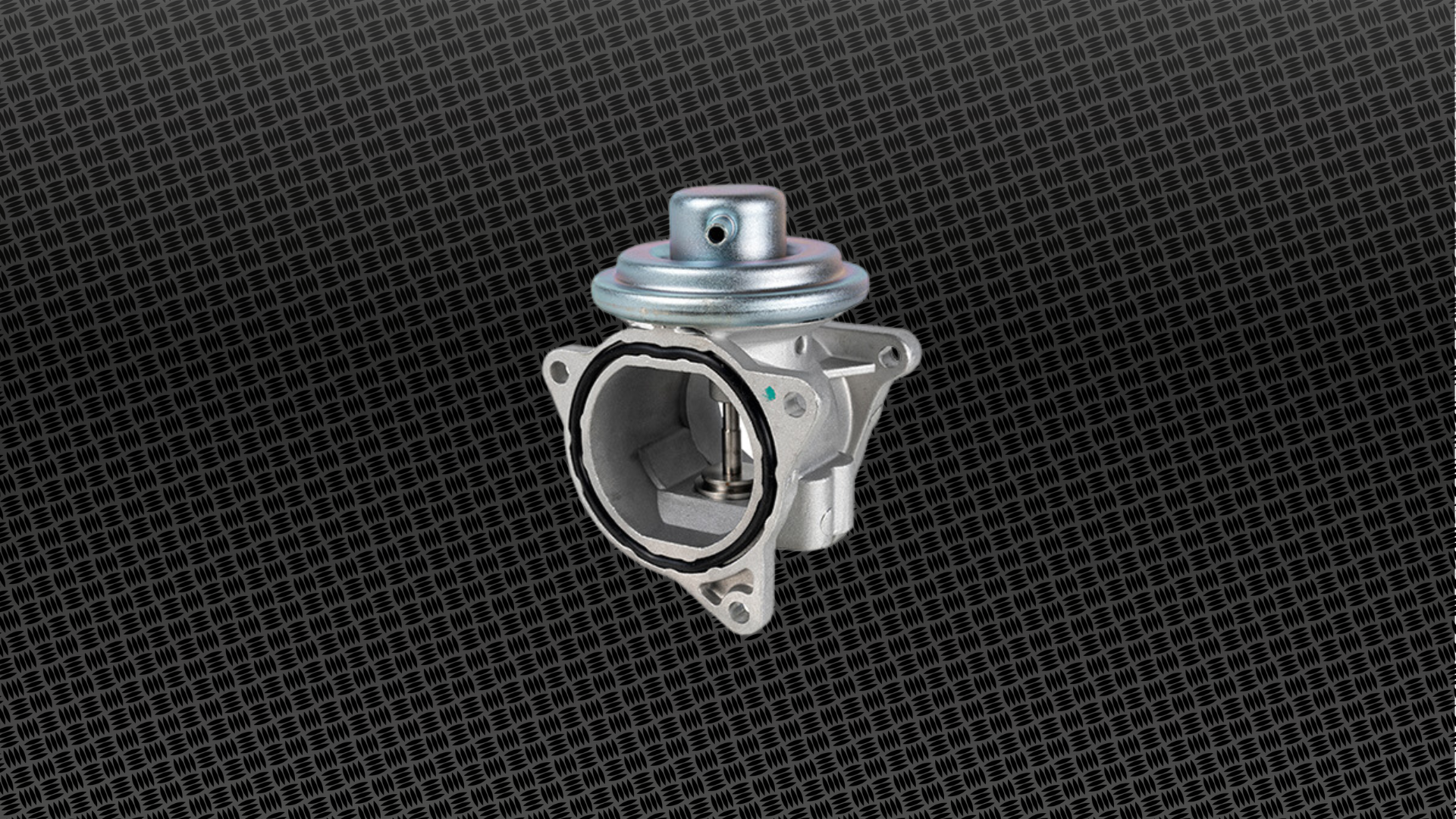
Do I need to clean the EGR valve?
The EGR valve is designed to send some of the polluting exhaust gases back into the intake manifold. The aim of this process is to lower combustion temperature and reduce NOx (nitrogen oxide) emissions in the exhaust pipe.
Exhaust gases are inert, so they do not react chemically during the combustion process and absorb some of the heat generated by combustion. This heat absorption in turn reduces the combustion temperature, resulting in a considerable reduction in NOx production. Nitrogen oxides are created during combustion when the ideal temperature is exceeded. Temperature control helps to regulate and reduce the gases emitted by vehicle exhausts.
EGR valves are installed in both petrol and diesel engines. Some diesel cars also incorporate a technology that enables them to operate with two EGR systems: a conventional system and a low-pressure system, to further reduce nitrogen oxide emissions.
Cars not equipped with a dual or low-pressure EGR system use other methods to reduce NOx emissions. The most common is the incorporation of an SCR (selective catalytic reduction) catalyst, which requires AdBlue for effective exhaust gas reduction.
For more efficient EGR valve operation, most modern EGR valves incorporate a radiator, which helps to further lower the temperature of the exhaust gases that are directed to the intake. A problem in the EGR circuit could cause a small coolant leak to reach the engine, resulting in white smoke emissions from the exhaust.
EGR valves operate in two ways – Some operate under a vacuum, while others are electrically actuated by a control system:
- Vacuum-controlled EGR systems are the fastest to reduce emissions. They operate at predetermined times according to engine speed and load, or via solenoid valves.
- Electric EGRs, on the other hand, offer much more precise control, as they have several opening points that allow the right amount of gas to pass through, depending on the driving conditions of each vehicle.
The technology downstream of EGR valves also includes a radiator. The function of the radiator is to reduce the temperature of the exhaust gases entering the intake manifold.
When engine combustion is incomplete (or all the fuel injected into the combustion chamber is burnt), large soot particles from the exhaust gases become trapped in the radiator, causing build-up and clogging. This reduces flow, resulting in inefficient emissions reduction. Normally, the EGR radiator must be removed for cleaning.
When the EGR valve is dirty and not working properly, it causes increased emissions, rough idling and running, high fuel consumption and contamination of other engine parts, including the intake manifold and particulate filter. A faulty or contaminated EGR system can prevent regeneration (self-cleaning) of the DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter) while the vehicle is on the road.
How do I clean the EGR valve without disassembling it?
Before starting to clean the EGR valve, it is necessary to identify its location in the circuit.
It is usually found in three places:
- Near the exhaust manifold
- Near or inside the intake system
- Between exhaust and intake
How to clean the EGR valve depending on its location?
- When the EGR valve is close to the exhaust, a tank treatment is recommended.
- When it is located close to or inside the intake system, an intake cleaner should be chosen.
- When located between the exhaust and the intake, neither fuel treatments nor intake cleaners are effective, so the EGR valve must be removed and cleaned manually.
Cleaning the EGR valve helps increase the flow of passing gases and to ensure that the system operates correctly.
A dirty valve prevents exhaust gas flow. This error is registered by the engine control unit and generates a fault code. If the required quantity of exhaust gas does not enter the intake manifold, nitrogen oxides are not effectively reduced.
Which Wynn’s products can I use to clean the EGR system?
-
For prevention; use Wynn’s Total Action Treatment in combination with Oil System Cleaner.
These products prevent build-up in the EGR circuit and clean the fuel and oil systems, helping to keep the combustion system and intake manifold clean. In other words, they will reduce soot deposits and consequently, emissions. They also improve vehicle performance.
-
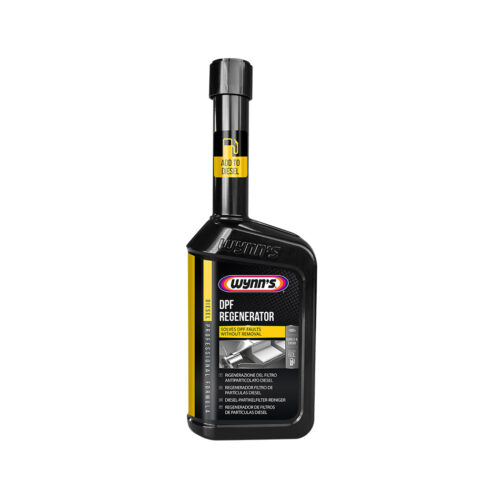
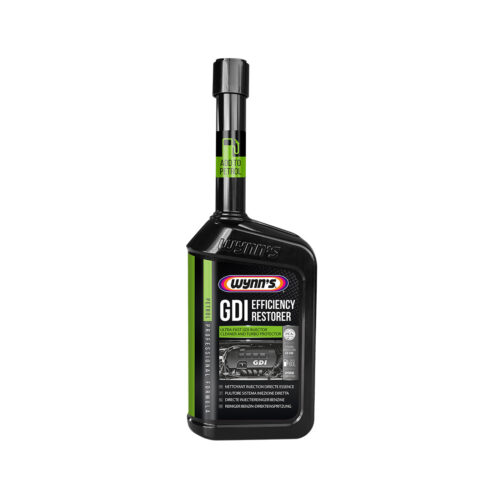
If the valve is close to the exhaust; use Diesel Extreme Injector Cleaner in combination with DPF Regenerator, for diesel vehicles and GDI Efficiency Restorer and Catalytic Converter and Oxygen Sensor Cleaner, for petrol vehicles.
If the EGR valves are located close to the exhaust, we recommend using Wynn’s Diesel Extreme Injector Cleaner or GDI Efficiency Restorer treatments, which work by adding it to the fuel tank. Combining this treatment with a catalytic converter such as Diesel DPF Regenerator or Catalytic Converter & Oxygen Sensor Cleaner will clean the injection by restoring injector spray patterns and lowering exhaust gas temperatures. The afterburner additive will clean EGR valves.
-
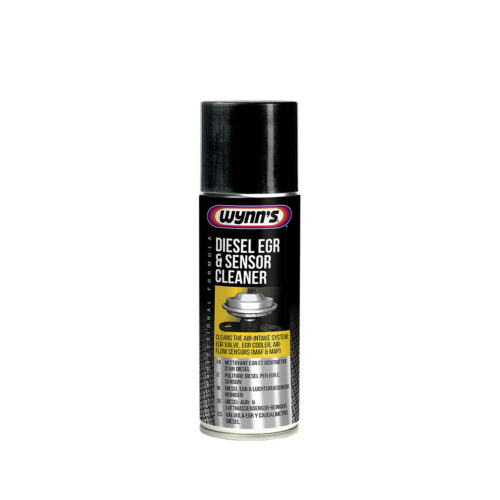
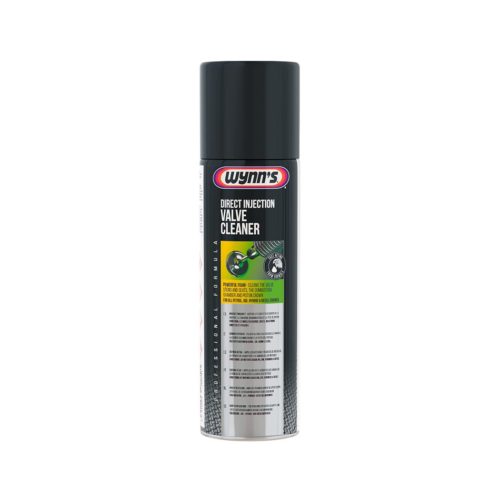
When the valve is located in the intake system; use EGR Extreme Cleaner or Direct Injection Valve Cleaner.
When using these products, be sure to apply only one treatment at a time through the intake on a running engine. In the event of a strange engine reaction, increased engine speed or running too high during application, stop the treatment and remove the EGR valve to clean it manually.
-
When the valve is between exhaust and intake; use DPF Off-Car Cleaner.
When the EGR valve is located between the exhaust and the intake, it requires manual cleaning. The most effective way to do this is to remove the valve from the vehicle and clean it with Wynn’s DPF Off Car Cleaner.









Leave A Comment